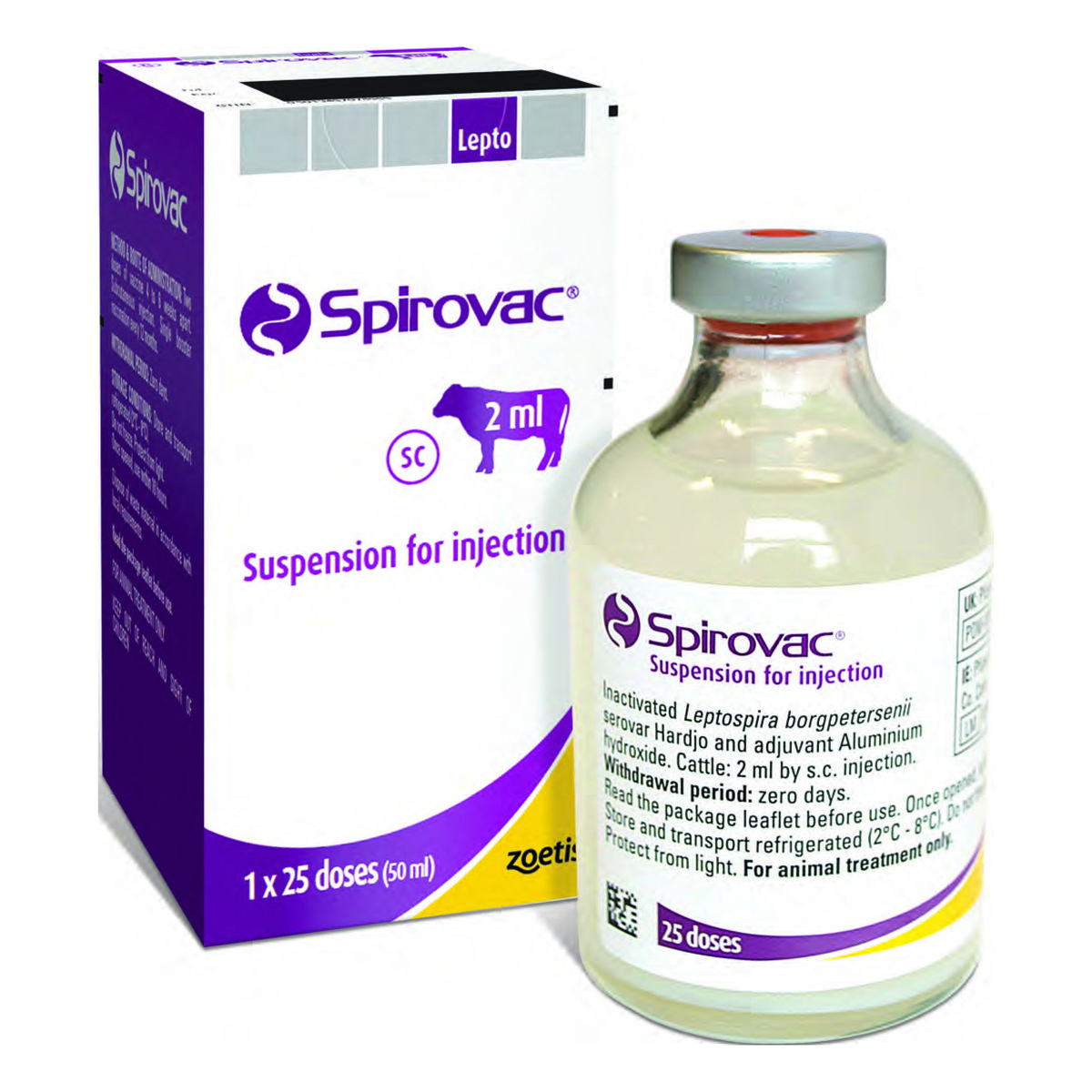
Description
Spirovac 2ml
Spirovac is an injectable vaccine that protects beef and dairy cattle against both strains of leptospiia hardjo, Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo (hardjo Prajitno) and L. borgpetersenii serovar hardjo (hardjo Bovis). Leptavoid-H
Treats And Controls:
Leptospiia hardjo, Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo (hardjo Prajitno) and L. borgpetersenii serovar hardjo (hardjo Bovis)
Dosage for cattle:
2 ml per animal. After the initial vaccination a second dose should be given no less than 4 weeks and no more than 6 weeks after.
| Body Weight | Dose Volume | Doses Per Pack |
| All Sizes | 2ml | 25 |
Always read the label and all enclosed information for Spirovac before administering to animals!
Active Ingredient:
Inactivated Leptospira borgpetersenii serovar Hardjo
Target Species:
Cattle
Administration Method:
Subcutaneous injection (under the skin)
Withdrawal Time:
There is no withdrawal time for this product
Leptospirosis in cattle
In a study carried out Eoin Lynch MVM it was found that 95% of all beef herds and 76% of all dairy herds have been exposed to leptospirosis infections and if an infection reaches an unvaccinated herd the effects can be severe. He advises that all herd owners should take action in the fight against this infection. Biotinmax 350g
What are the signs of a Leptospirosis infection.
- Reduction in milk produced
- Abortion which can occur in the late stages of pregnancy
- Low conception rates
- Weak calves are born
- High temperatures in cattle
- Flaccid, empty udders
- Sudden drop in yield
How do herds become infected with Leptospirosis?
Leptospirosis is mainly spread through urine, this means all grazing cattle are in danger of becoming infected. The infection can spread where cattle drink from a natural water source such as a river running through land. Buying in unvaccinated cattle can bring the infection to your herd. The use of a stock bull can spread the infection. Sheep if co-grazing with cattle can spread the infection without showing any signs of infection themselves.
Vaccinating cattle can have increased conception rates.
Another study has shown that vaccinated cattle have a higher conception rate at first service. Herds were divided into two groups, one group was vaccinated and the other was not. The conception rate in vaccinated groups was 51% where the conception rate in the un-vaccinated group was 31%


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.